Configure your local setup
Whether you currently use dbt platform or self-host with Fusion, or you’re a dbt Core user upgrading to Fusion, follow the instructions on this page to:
If you're new to dbt or getting started with a new project, you can skip this page and check out our Quickstart for the dbt Fusion Engine to get started with the dbt extension.
The steps differ slightly depending on whether you use dbt platform or self host with Fusion.
- dbt platform — You’ll mirror your dbt platform environment locally to unlock Fusion-powered features like Mesh, deferral, and so on. If your project has environment variables, you'll also set them locally to leverage the VS Code extension's features.
- Self-hosted — When you self-host with Fusion or are upgrading from dbt Core to Fusion, you’ll most likely already have a local setup and environment variables. Use this page to confirm that your existing local setup and environment variables work seamlessly with the dbt Fusion Engine and VS Code extension.
Prerequisites
- dbt Fusion Engine installed
- Downloaded and installed the dbt VS Code extension
- Basic understanding of Git workflows and dbt project structure
- Developer or analyst license if you're using dbt platform
Prepare your local setup
In this section, we'll walk you through the steps to prepare your local setup for the dbt VS Code extension. If you're a dbt platform user that installed the VS Code extension, follow these steps. If you're a self-hosted user, you most likely already have a local setup and environment variables but can confirm using these steps.
- Clone your dbt project repository from your Git provider to your local machine. If you use dbt platform, clone the same repo connected to your project.
- Ensure you have a dbt
profiles.ymlfile. This file defines your data warehouse connection. If you don't have one, rundbt initin the terminal to configure your adapter. - Validate your
profiles.ymland project configuration by runningdbt debug. - Add a
dbt_cloud.ymlfile from the dbt platform Account settings:- Navigate to Your profile -> VS Code Extension -> Download credentials.
- Download the
dbt_cloud.ymlfile with your Personal access Token (PAT) included and place it in the~/.dbt/directory. This then registers and connects the extension to dbt platform and enables platform features such as Mesh and deferral. - Check the
project_idin yourdbt_project.ymlfile matching the project you're working on.
- Confirm connection from your workstation (like running
dbt debugin the terminal). Your local computer connects directly to your data warehouse and Git.- dbt platform users: Ensure your laptop/VPN is allowed; dbt platform IPs no longer apply. Check with your admin if you have any issues.
- dbt Core users: This has likely already been configured.
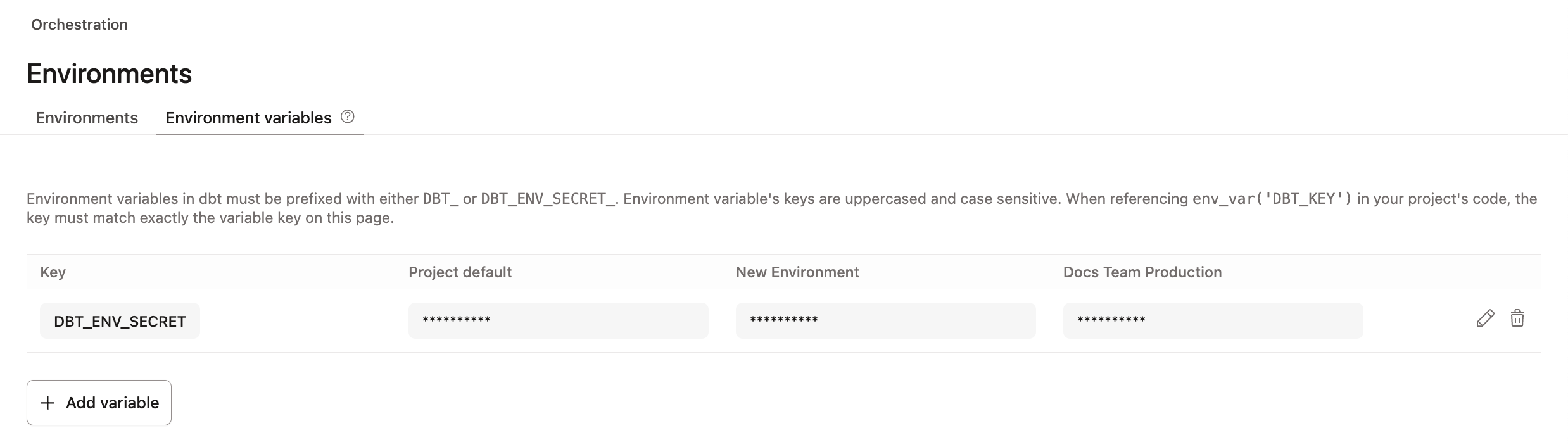
- (Optional) If your project uses environment variables, find them in the dbt platform and set them in VS Code or Cursor.
- dbt platform users: Copy any environment variables from Deploy → Environments → Environment variables tab in dbt platform. Masked secrets are hidden. Work with your admin to get those values.
Set environment variables locally
Environment variables are used for authentication and configuration.
This section is most relevant for dbt VS Code extension and dbt platform users who have environment variables configured as part of their workspace setup. If you’re using Fusion locally, you can also install the VS Code extension and use its features and actions — you just may not need to configure these variables unless your setup specifically requires them.
The following table shows the different options and when to use them:
| Location | Affects | Session state | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell profile | Terminal | ✅ Permanent | Variables remain active globally and available across terminal sessions. |
| VS Code/Cursor settings | Extension menus + LSP | ✅ Per VS Code/Cursor profile | Editor-only workflows using the extension menu actions. |
| Terminal session | Current terminal only | ❌ Temporary | One off testing. |
If you want to use both the VS Code extension menus and terminal to run dbt commands, define your variables in the shell profile and VS Code/Cursor settings so they remain active in the terminal globally and in VS Code/Cursor.
Configure at the OS or shell level
Define variables once at the OS or shell level to ensure they're available to all terminal sessions. Even if you close a terminal window, the variables will remain available to you.
- Mac / Linux
- Windows
- Open your shell configuration file in a text editor using the following commands (If the file does not exist, create it using a text editor using
vi ~/.zshrcorvi ~/.bashrc):open -e ~/.zshrc ## for zsh (macOS)
nano ~/.bashrc ## for bash (Linux or older macOS) - A file will open up and you can add your environment variables to the file. For example:
- For zsh (macOS):
## ~/.zshrc
export DBT_ENV_VAR1="my_value"
export DBT_ENV_VAR2="another_value" - For bash (Linux or older macOS):
## ~/.bashrc or ~/.bash_profile
export DBT_ENV_VAR1="my_value"
export DBT_ENV_VAR2="another_value"
- For zsh (macOS):
- Save the file.
- Start a new shell session by closing and reopening the terminal or running
source ~/.zshrcorsource ~/.bashrcin the terminal. - Verify the variables by running
echo $DBT_ENV_VAR1andecho $DBT_ENV_VAR2in the terminal.
If you see the value printed back in the terminal, you're all set! These variables will now be available:
- In all future terminal sessions
- For all dbt commands run in the terminal
There are two ways to create persistent environment variables on Windows: through PowerShell or the System Properties.
The following steps will explain how to configure environment variables using PowerShell.
PowerShell
- Run the following commands in PowerShell:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("DBT_ENV_VAR1","my_value","User")
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("DBT_ENV_VAR2","another_value","User")
- This saves the variables permanently for your user account. To make them available system-wide for all users, replace "User" with "Machine" (requires admin rights).
- Then, restart VS Code or select Developer: Reload Window for changes to take effect.
- Verify the changes by running
echo $DBT_ENV_VAR1andecho $DBT_ENV_VAR2in the terminal.
System properties (Environment Variables)
- Press Start → search for Environment Variables → open Edit the system environment variables.
- From the Advanced tab of the System Properties, click Environment Variables….
- Under User variables, click New….
- Add the variables and values. For example:
- Variable name:
DBT_ENV_VAR1 - Variable value:
my_value
- Variable name:
- Repeat for any others, then click OK.
- Restart VS Code or Cursor.
- Verify the changes by running
echo $DBT_ENV_VAR1andecho $DBT_ENV_VAR2in the terminal.
Configure in the VS Code extension settings
To use the dbt extension menu actions/buttons, you can configure environment variables directly in the VS Code User Settings interface or in any .env file at the root level.
- Configuring in the User Settings works with the dbt extension buttons and menus (for LSP, "Show build menu," and so on).
- Not inherited by the VS Code terminal or external shells.
- Running a dbt command in the terminal won't fetch or use these variables.
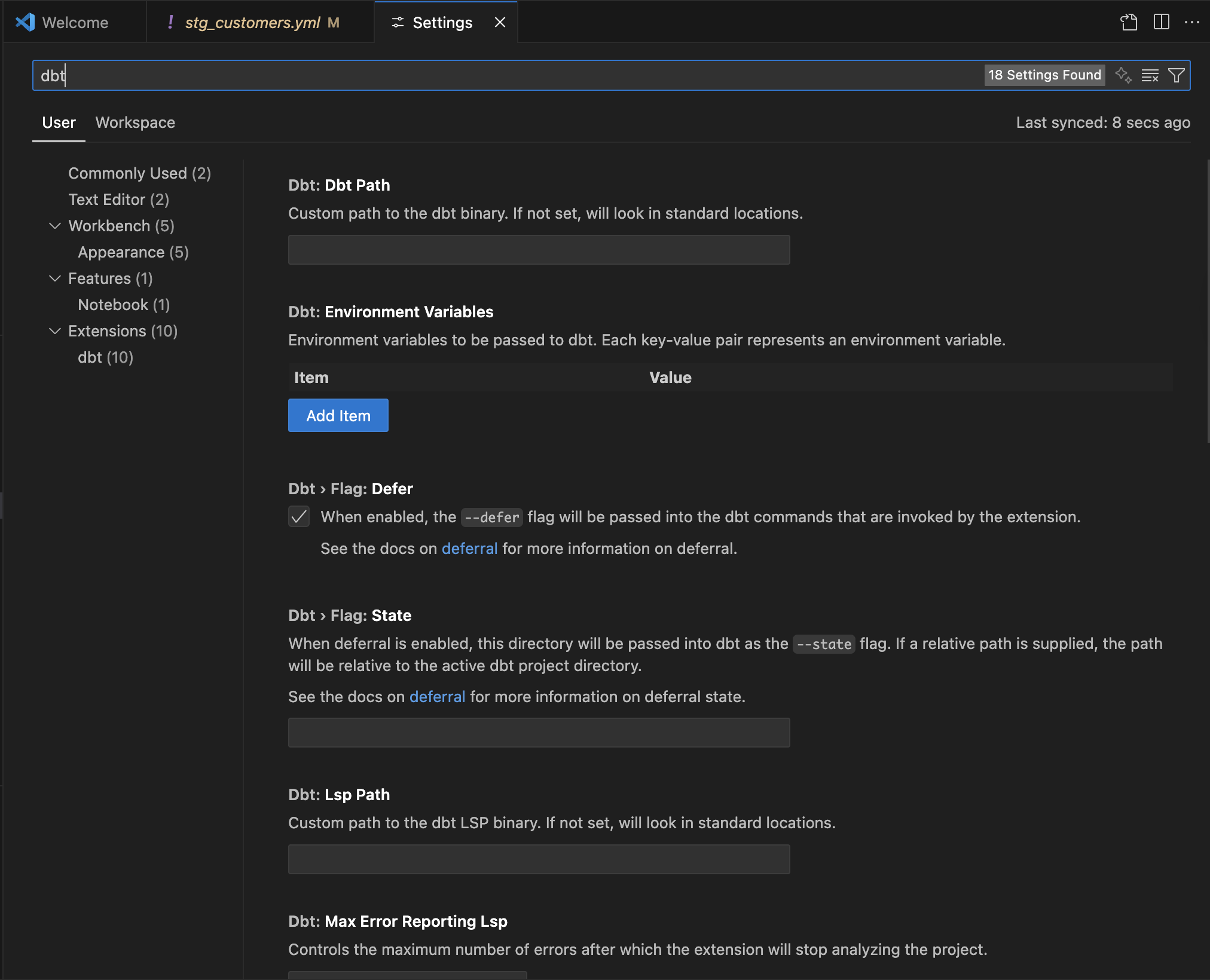
To configure environment variables in VS Code/Cursor:
- Open User Settings
- Open .env file
- Open the Command Palette (Cmd + Shift + P for Mac, Ctrl + Shift + P for Windows/Linux).
- Then select either Preferences: Open User Settings in the dropdown menu.
- Open the VS Code user settings page.
- Search for
dbt.environmentVariables. - In the dbt:Environment Variables section, add your item and value for the environment variables.
- Click Ok to save the changes.
- Reload the VS Code extension to apply the changes. Open the Command Palette and select Developer: Reload Window.
- Verify the changes by running a dbt command and checking the output.
- In your dbt project, create a
.envfile at the root level (same level as yourdbt_project.ymlfile). - Add your environment variables to the file. For example:
DBT_ENV_VAR1=my_value
DBT_ENV_VAR2=another_value - Save the file.
- Reload the VS Code extension to apply the changes.
- Verify the changes by running a dbt command using the extension menu button on the top right corner and checking the output.
Configure in the terminal session
Configure environment variables in the terminal session using the export command. Something to keep in mind:
- Doing so will make variables visible to commands that run in that terminal session only.
- It lasts only for the current session and opening a new terminal will lose the values.
- The built-in dbt VS Code extension buttons and menus will not pick these up.
To configure environment variables in the terminal session:
-
Run the following command in the terminal, replacing
DBT_ENV_VAR1andtest1with your own variable and value.- Mac / Linux
- Windows Cmd
- Windows PowerShell
export DBT_ENV_VAR1=test1Refer to Microsoft's documentation for more information on the
setcommand.set DBT_ENV_VAR1=test1Refer to Microsoft's documentation for more information on the
$env:syntax.$env:DBT_ENV_VAR1 = "test1" -
Verify the changes by running a dbt command and checking the output.
Configure the dbt extension
After installing the dbt extension and configuring your local setup, you may want to configure it to better fit your development workflow:
- Open the VS Code settings by pressing
Ctrl+,(Windows/Linux) orCmd+,(Mac). - Search for
dbt. On this page, you can adjust the extension’s configuration options to fit your needs.
Next steps
Now that you've configured your local environment, you can start using the dbt extension to streamline your dbt development workflows. Check out the following resources to get started:
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.